
The Science Behind Pet Aging: Understanding Dog Years
The notion that one dog year equals seven human years has been widely accepted for decades, but it oversimplifies the complex process of canine aging. Dogs, like humans, do not age at a constant rate, and the pace of their development is influenced by factors such as breed, size, genetics, and overall health.
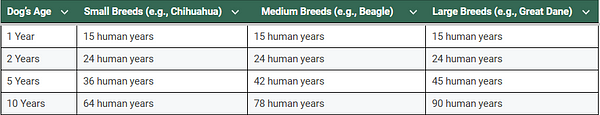
2 Years: Equivalent to about 24 human years.
Medium breeds: Equivalent to about 42 human years.
Large breeds: Equivalent to about 45 human years.
Medium breeds: Equivalent to about 78 human years.
Large breeds: Equivalent to about 90 human years.
Why the “7-Year Rule” is Misleading
The traditional 7-year formula was likely created as a quick reference, but it fails to account for the varying lifespans and growth rates of different dog breeds. For example, small dogs like Chihuahuas tend to live longer than larger breeds like Great Danes. Smaller dogs mature faster in their early years but then age more slowly compared to larger breeds, which experience rapid growth and aging throughout their shorter lifespansAge Chart for Dogs
1 Year: Equivalent to about 15 human years.2 Years: Equivalent to about 24 human years.
5 Years:
Small breeds: Equivalent to about 36 human years.Medium breeds: Equivalent to about 42 human years.
Large breeds: Equivalent to about 45 human years.
10 Years:
Small breeds: Equivalent to about 64 human years.Medium breeds: Equivalent to about 78 human years.
Large breeds: Equivalent to about 90 human years.
What This Means for Pet Owners
Understanding your dog’s “human age” is more than just a fun calculation it provides valuable insights into their health and care needs:
1. Young Dogs (0–2 Years)
Equivalent to teenage humans, they require training, socialization, and proper nutrition to thrive.
Smaller breeds tend to live longer than larger breeds. This is due to the faster growth rates and higher incidence of age-related diseases in larger dogs.
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, strong muscles, and overall fitness.
Regular veterinary check-ups can help detect any health issues early. Preventive care is crucial for maintaining your pet’s health.
1. Young Dogs (0–2 Years)
Equivalent to teenage humans, they require training, socialization, and proper nutrition to thrive.
2. Middle-Aged Dogs (3–6 Years)
This stage mirrors human adulthood, where maintaining a healthy weight, regular vet check-ups, and exercise are key.3. Senior Dogs (7+ Years)
Like senior humans, older dogs may face issues such as arthritis, reduced energy, and changes in dietary needs. Regular monitoring and adjustments in lifestyle can help them age gracefully.Factors Affecting Pet Aging
Several factors influence how quickly your pet ages:Breed and Size:
1. Dogs:Smaller breeds tend to live longer than larger breeds. This is due to the faster growth rates and higher incidence of age-related diseases in larger dogs.
2 . Diet and Exercise:
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can significantly extend your pet’s lifespan.Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, strong muscles, and overall fitness.
3. Genetics:
Some pets are genetically predisposed to certain health conditions that can affect their lifespan. Regular vet check-ups can help manage these conditions.4. Environment:
A safe and stress-free environment can contribute to a longer, healthier life for your pet. Ensure they have a comfortable living space and access to outdoor areas for exercise and mental stimulation.Tips for Keeping Your Pet Healthy
1. Regular Vet Check-ups:Regular veterinary check-ups can help detect any health issues early. Preventive care is crucial for maintaining your pet’s health.
2. Balanced Diet:
Feed your pet a balanced diet suitable for their age and activity level. Consult your vet for recommendations on the best food for your pet.3. Exercise:
Ensure your pet gets enough exercise to maintain a healthy weight and strong muscles. This can include walks, playtime, and interactive toys.4. Mental Stimulation:
Provide toys and activities that keep your pet mentally stimulated. Puzzle toys, training sessions, and interactive play can keep their minds sharp.5. Preventive Care:
Keep up with vaccinations, flea and tick prevention, and dental care. Regular grooming can also help detect any skin or coat issues early.Understanding Senior Pets
As your pet ages, their needs change. Senior pets may require special diets, more frequent vet visits, and adjustments to their exercise routines.
Signs of Aging in Dogs
Decreased Energy: Senior pets may become less active and tire more easily.Graying Fur: Just like humans, pets can develop gray hair as they age.
Joint Issues: Older pets may experience joint pain and stiffness, making it harder for them to move around.
Dental Problems: Senior pets are more prone to dental issues, which can affect their overall health.
Changes in Behavior: Aging pets may become more anxious, irritable, or disoriented.
Caring for Senior Pets
Diet Adjustments: Senior pets may benefit from diets formulated for their age group, which often include joint supplements and easier-to-digest ingredients.Regular Check-ups: More frequent vet visits can help monitor any age-related health issues.
Comfort and Mobility: Provide comfortable bedding and ramps or steps to help senior pets navigate their environment more easily.
Mental Stimulation: Continue to engage your senior pet with mental stimulation to keep their minds active and sharp.
Conclusion
Understanding your pet’s age in human years can help you provide better care and anticipate their needs as they grow older. Whether you have a playful puppy, knowing their age equivalents can deepen your bond and ensure they live a long, healthy life.
For more insights and tips on pet care, stay tuned to our blog. Share your pet’s story with us in the comments below!
Comments
Post a Comment